
Such nervous system changes can be correlated with emotional responses to interaction events.
#PUPIL DILATION SKIN#
Changes in perspiration are measured by galvanic skin response measurements to detect changes in electrical conductivity. Examples include changes in heart rate, respiration, perspiration, and eye pupil dilation. Biometrics are about detection and measurement of autonomic or involuntary bodily changes triggered by nervous system responses to emotional impact within interaction events. The use of instrumented measurement of physiological responses in participants is called biometrics. Pyla, in The UX Book, 2012 Bio-metrics to detect physiological responses to emotional impact However, considering the ease with which we can collect this data, UX researchers should consider the opportunity. It would be bad practice to only use pupil dilation to make inferences about cognitive processes and user experience, as the story is incomplete. Therefore, caution must be made when interpreting the results of pupil dilation data.Īs with other UX research methods, it is important to combine metrics with pupil dilation.

Jagdish Sheth, a marketing professor at Emory University, explains: “There no scientific way to establish whether measured interest or anxiety” ( Fong, 2012). Pupil dilation has been used to assess a number of cognitive functions, including fatigue, racial biases, and depression however, it is impossible to tell what changes in pupil size mean without considering the context in which these changes occur ( Powell & Schirillo, 2011).

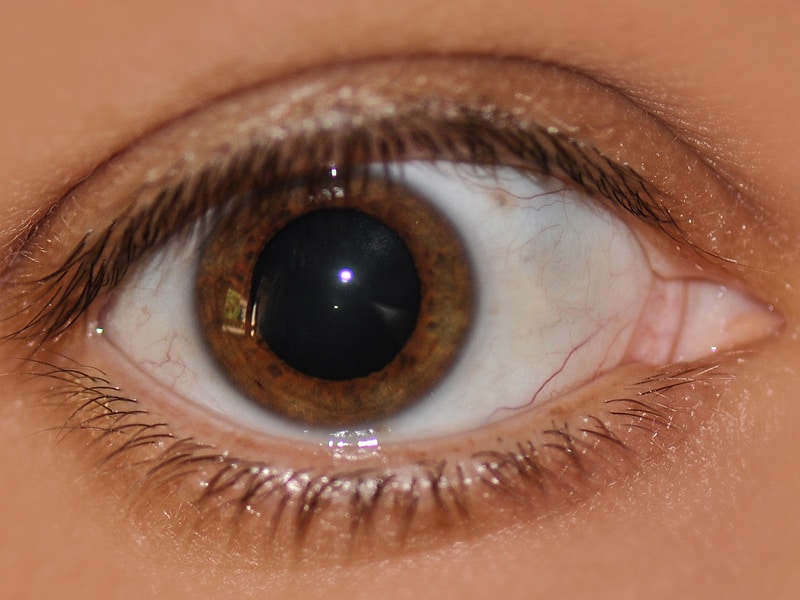
Book an appointment here.It has been hypothesized that increased blinking is associated with negative feelings and on the contrary, decreases with pleasant psychological states. In each of these cases, fixed dilated pupils are an indication that something is not quite right with your eyes and needs looking into by an optician – the earlier the better too. It can be painful and make you sensitive to light because the pupils stay dilated. Uvetis or iritis– there are different types of inflammation which can affect the eye depending on the area of the uvea (the middle layer of the eye which includes the iris) that is inflamed, and how long it lasts for. If the pressure rises significantly it can affect the iris’s ability to control the pupil. Glaucoma – affects the optic nerve and causes pressure to build up in your eye. This is a sign that a disease is affecting the retina or optic nerve. Relative afferent pupillary defect (RAPD) – in this case, the pupils actually dilate in response to light instead of shrinking – in one or both eyes. This is because when we see someone attractive our brains release dopamine which can cause our pupils to dilate.ĭilated pupils can also be an indication of other, more serious eye conditions and infections, including: Often used in advertising to demonstrate beauty, dilated pupils are a sign that we are attracted to someone. This is why you often see doctors shining lights in a patient’s eyes to see if the pupils constrict (as they should) or stay dilated. If you have an injury or disease that affects your brain (for example head trauma, stroke or tumour) the pressure can build in your head and affect the ability of the muscles in your iris to control your pupil. If you injure your eye it’s important to seek medical attention. Eye injuryĪn eye injury can damage nerves or the muscles in your iris that control your pupil size. In some cases, infections can happen after eye surgery that affect the iris’s ability to control the pupils, for example, after cataract surgery or corneal transplant. Some infections of the eye and nervous system can affect the ability to control the pupils, an example would be the virus that causes chickenpox or shingles. If you notice your eyes are staying dilated as a result of medication, you should go back to see your GP. Some illegal drugs can also have the same effect. These include some antidepressants, antihistamines, decongestants and even motion sickness tablets. If your pupils dilate without any change in light it is called ‘mydriasis’ and can be caused by a variety of things, including: MedicinesĪ few medicines can affect the iris muscles and prevent them from constricting your pupils when light hits them. A healthy pupil size will normally range from 2-4mm in normal light up to 8mm in low light. In low light, your pupils open up (dilate) to let in more light, but when it’s bright, they get smaller (constrict) to let in less light. Your pupils change in size depending on how bright the light is around you. The muscles in your iris (the coloured part of your eye ) control your pupil size.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
